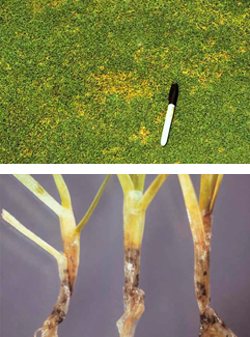
Anthracnose is a fungal disease that attacks grass plants, normally only Annual meadow grass (poa annua) but occasionally other grasses will show symptom when they are under environmental stress. It is triggered by low nutrition and compaction leading to reduced turf vigour.
Symptoms | Foliar Blight: Irregular patches of turf will turn a tan colour and die. Small black acervuli with a hair like setae will be visible with a x10 hand lens. |
Susceptible grass species | Foliar Blight: It will affect all grass types but the most susceptible is annual meadow-grass. |
When does it appear? | Foliar Blight: In the Summer. |
Climate Conditions | Foliar Blight: When its warm and wet. |
Turf condition | Turf would have to be highly stressed with low fertility (nitrogen especially but also potassium and phosphorous imbalances) When the turf has a moist surface, but dry soil and cut at a low height. |
Cause
Anthracnose attacks grass plants, normally only Annual meadow grass (poa annua) but occasionally other grasses will show symptom when they are under environmental stress.
Disease triggered by low nutrition and compaction leading to reduced turf vigour.
Anthracnose is usually prevalent in late summer but can be present at any time of year.
Once disease reaches basal rot stage fungicides are no longer effective for control of disease but should be applied to prevent further attack.
Cultural Control
Turf should have sufficient nutritional input, particularly coming into the end of the summer.
Using a slow release fertiliser late in the season ensures that adequate nutrition is in the soil to promote a healthy turf.
Avoid low heights of cut as they add to turf stress.
Minimise mechanical cultivation during periods of stress.
Aerate to relieve compaction and improve oxygen levels.
Irrigate in the morning to minimise long periods of leaf wetness over night.
Use a penetrating wetting agent to move water through soil profile and to keep surface dry.
Chemical Control
If cultural control is not effective, anthracnose control can be achieved by the use of chemicals
Apply a preventative fungicide such as Dedicate (Tebuconazole and Trifloxystrobin) or Ascernity (Solatenol and Difenoconazole) when risk is high (usually around early August).
If Anthracnose is active apply either Dedicate (Tebuconazole and Trifloxystrobin) or Medallion TL (Fludioxonil) depending on time of year, last fungicide applied and temperatures.
Always add Prestige Super Recovery to each fungicide application.
Notes:
Use fungicides as part of an IPM programme and be aware of causing resistance to one chemical group by its regular use.
Use plant protection safely. Always read the label and product information before use














